📘 Compound Financial Instruments under IFRS 9 & Ind AS 109
1. 🌐 Definition
A compound financial instrument (CFI) is a single contract that contains both:
- Liability component → obligation to deliver cash/financial asset (e.g., interest, principal repayment).
- Equity component → residual interest or option to convert into equity (e.g., conversion option).
👉 Classic example: Convertible bonds/debentures
2. 🏗️ Initial Recognition
Both IFRS 9 and Ind AS 109 require split accounting:
- Step 1: Measure liability component → present value of contractual cash flows discounted at market rate for similar debt without conversion option.
- Step 2: Equity component = residual (issue proceeds – liability component).
- Step 3: Allocate transaction costs proportionately between components.
3. 📊 Subsequent Measurement
- Liability component:
- Measured at amortized cost using the effective interest method.
- Interest expense recognized in P&L.
- Equity component:
- Recognized in equity (often “Other Equity”).
- Not remeasured after initial recognition.
4. 🧮 Numerical Example – Convertible Bond
i. Terms
- Issue proceeds: ₹1,000,000
- Coupon rate: 6% annually
- Term: 3 years
- Market rate for similar non-convertible debt: 10%
ii. Initial Recognition
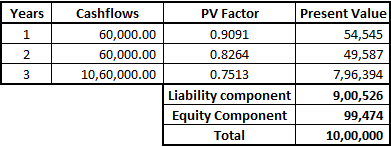
iii. Journal Entry:
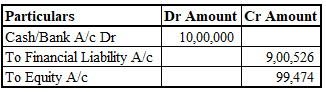
iv. Subsequent Recognition (Effective Interest Method)
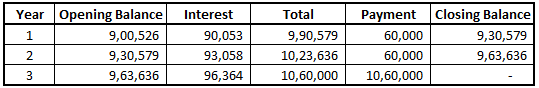
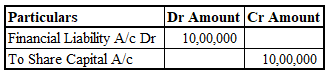
v. At Conversion
- Liability derecognized (₹1,000,000).
- Equity shares issued.
- Equity component (₹99,474) remains in reserves.
- Journal Entry:
5. 📝 Disclosure Requirements
Both standards require disclosure of:
- Nature and terms of instrument.
- Accounting policies for separation.
- Carrying amounts of liability and equity components.
- Impact on reserves and earnings.
✅ Key Takeaways
- CFIs must be split into liability and equity at inception.
- Liability grows under effective interest method; equity remains fixed.
- Conversion leads to derecognition of liability and issuance of shares.
- Both IFRS 9 and Ind AS 109 follow the same conceptual framework, ensuring transparency in reporting.
Finegal Tech Solution
0